

If it’s a backup server why not build a system around an CPU with an integrated GPU? Some of the APUs from AMD aren’t half bad.
Particularly if it’s just your backup… and you can live without games/video/acceleration while you repair your primary?


If it’s a backup server why not build a system around an CPU with an integrated GPU? Some of the APUs from AMD aren’t half bad.
Particularly if it’s just your backup… and you can live without games/video/acceleration while you repair your primary?


Is there a reason you need a dual book instance instead of a VM or even WINE?
Unless you need direct access to hardware and if you have enough RAM, you can probably avoid dual booting altogether.


Good enough? I mean it’s allowed. But it’s only good enough if a licensee decides your their goal is to make using the code they changed or added as hard as possible.
Usually, the code was obtained through a VCS like GitHub or Gitlab and could easily be re-contributed with comments and documentation in an easy-to-process manner (like a merge or pull request). I’d argue not completing the loop the same way the code was obtained is hostile. A code equivalent of taking the time (or not) to put their shopping carts in the designated spots.
Imagine the owner (original source code) making the source code available only via zip file, with no code comments or READMEs or developer documentation. When the tables are turned - very few would actually use the product or software.
It’s a spirit vs. letter of the law thing. Unfortunately we don’t exist in a social construct that rewards good faith actors over bad ones at the moment.


As someone who worked at a business that transitioned to AGPL from a more permissive license, this is exactly right. Our software was almost always used in a SaaS setting, and so GPL provided little to no protection.
To take it further, even under the AGPL, businesses can simply zip up their code and send it to the AGPL’ed software owner, so companies are free to be as hostile as possible (and some are) while staying within the legal framework of the license.


Pros:
Cons:


pfBlockerNG at the network edge and ublockorigin on devices.


Pijul is a very exciting project. I’ve wanted to try it for months buy haven’t found the time.
Hard to tell from first glance but my guess would be this is fallout from the ongoing xz drama. Here: https://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2024/03/29/4
I’m on iOS and do the same thing.
The WireGuard app has a setting to “connect on demand”. It’s in the individual connections/configurations.
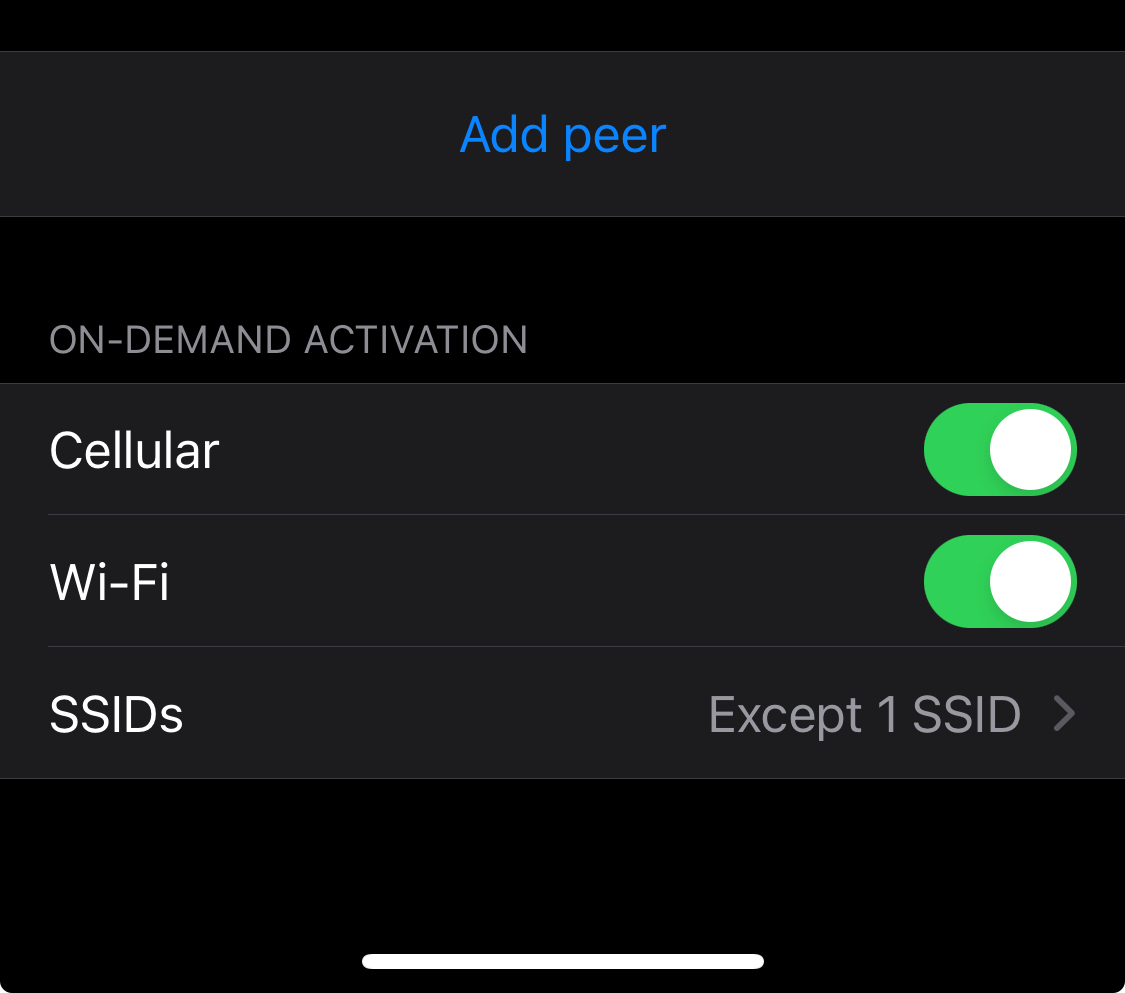
You can then set either included or excluded SSIDs. There’s also an option to always connect when you’re on mobile/cellular data.
I imagine the Android app is similar.


Neat, I’ll have to look it up. Thanks for sharing!


Nextcloud isn’t exposed, only a WireGuard connection allows for remote access to Nextcloud on my network.
The whole family has WireGuard on their laptops and phones.
They love it, because using WireGuard also means they get a by-default ad-free/tracker-free browsing experience.
Yes, this means I can’t share files securely with outsiders. It’s not a huge problem.


You’re conferring a level of agency where none exists.
It appears to “understand.” It appears to be “knowledgeable. “
But LLMs do neither of those things.
Take this note from an OpenAI dev:

It’s that these models have leveraged so much data they’ve been able to map out relationships between words (or images) in way as to be able to generate what seem like new versions of those things.
I grant you that an LLM has more base level knowledge than any one human, but again this is thanks to terrifyingly large dataset and a design that means it can access this data reasonably reliably.
But it is still a prediction model. It just has more context, better design and (most importantly) data to make predictions at a level never before seen.
If you’ve ever had a chance to play with a model at level where you can control some of its basic parameters it offers a glimpse into just how much of a prediction machine it can be.
My favourite game for a while was to give midjourney a wildly vague prompt but crank the chaos up to 100 (literally the chaos flag at the highest level) to see what kind of wild connections exist but are being filtered out during “normal” use.
The same with the GPT-3.5 API in the “early days” - you could return multiple versions of the response and see the sausage being made to a very small degree.
It doesn’t take away from the sense of magic using these tools. It just helps frame what’s going on under the hood.


Update: I went and had a look and there’s a Terraform provider for OPNSense under active development - it covers firewall rules, some unbound configuration options and Wireguard, which is definitely more than enough to get started.
I also found a guide on how to replicate pfBlocker’s functionality on OPNSense that isn’t terribly complicated.
So much of my original comment below is less-than-accurate.
OPNSense is for some, like me, not a viable alternative. pfBlockerNG in particular is the killer feature for me that has no equivalent on OPNSense. If it did I’d switch in a heartbeat.
If I have to go without pfBlockerNG, then I’d likely turn to something that had more “configuration as code” options like VyOS.
Still, it’s nice to know that a fork of a fork of m0n0wall can keep the lights on, and do right by users.


If you backup your config now, you’d be able to apply the config to CE 2.7.x.
While this would limit you to an x86 type device, you wouldn’t be out of options.
I am an owner of an SG-3100 as well (we don’t use it anymore), but that device was what soured me on Netgate after using pfSense on a DIY router at our office for years…
I continued to use pfSense because of the sunk costs involved (time, experience, knowledge). This is likely the turning point.


Cluster of Pi4 8GBs. Bought pre-pandemic; love the little things.
Nomad, Consul, Gluster, w/ TrueNas-backed NFS for the big files.
They do all sorts of nifty things for us including Nightscout, LanguageTool OSS, monitoring for ubiquiti, Nextdrive, Grafana (which I use for home monitoring - temps/humidity with alerts), Prometheus & Mimir, Postgres, Codeserver.
Basically I use them to schedule dockerized services I want to run or am interested in playing with/learning.
Also I use Rapsberry Pi zero 2 w’s with Shairport-sync (https://github.com/mikebrady/shairport-sync ) as Airplay 2 streaming bridges for audio equipment that isn’t networked or doesn’t support AirPlay 2.
I’m not sure I’d buy a Pi4 today; but they’ve been great so far.
As someone who runs a self-hosted mail service (for a few select clients) in AWS, this comment ring true in every way.
One thing that saved us beyond SPF and DKIM was DMARC DNS records and tooling for diagnosing deliverability issues. The tooling isn’t cheap however.
But even then, Microsoft will often blacklist huge ranges of Amazon EIPs and if you’re caught within the scope of that range it’s a slow process to fix.
Also, IP warming is a thing. You need to start slow and at the same time have relatively consistent traffic levels.
Is it worth it, not really no - and I don’t think I’d ever do it again.


deleted by creator
The only way to ensure privacy is something like PGP. Encrypt before you send. Heck you could even encrypt before you put the contents into a message body.
With self hosted, the messages themselves aren’t encrypted at rest and they are clear text between hops even if those hops support TLS in transit.
Ultimately the right answer for you will hinge on what your definition and level of privacy is.


Snaps I get, but Ubuntu? Aside from an asinine application process to get hired a Canonical, they did a lot to push for a more straightforward Linux desktop experience. Their time has passed, but cancer is a bit too much for me, considering all the fantastic offshoots.
Context: I came to Ubuntu from Gentoo. Debian before that and a brief flirt with the hot fantastic mess that was Mandrake when I first discovered Linux.
Found the other NixOS user. ;)